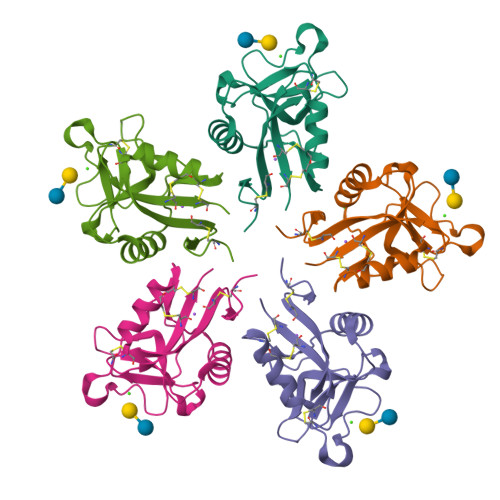
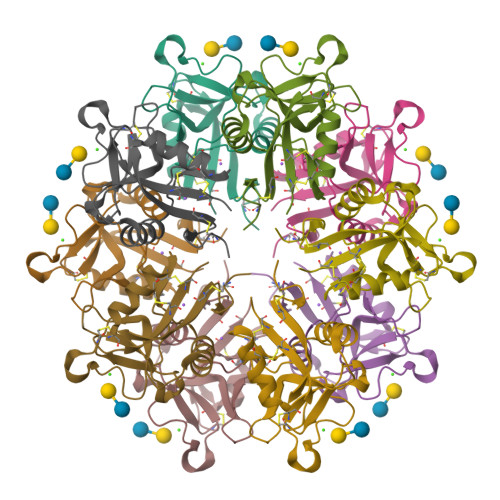
X-ray Crystal Structure of a Galactose-Specific C-Type Lectin Possessing a Novel Decameric Quaternary Structure.
Walker, J.R., Nagar, B., Young, N.M., Hirama, T., Rini, J.M.(2004) Biochemistry 43: 3783-3792
- PubMed: 15049685
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/bi035871a
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1JZN, 1MUQ - PubMed Abstract:
Rattlesnake venom lectin (RSL) from the western diamondback rattlesnake (Crotalus atrox) is an oligomeric galactose-specific C-type lectin. The X-ray crystal structure of RSL, in complex with lactose and thiodigalactoside, at 2.2 and 2.3 A resolution, respectively, reveals a decameric protein composed of two 5-fold symmetric pentamers arranged in a staggered, back-to-back orientation. Each monomer corresponds to a single canonical C-type lectin carbohydrate recognition domain devoid of accessory domains and is disulfide-bonded to a monomer in the other pentamer. The structure is the first example of that of a carbohydrate complex of a vertebrate galactose-specific C-type lectin. The 10 carbohydrate-binding sites, located on the rim of the decamer, suggest a role for multivalent interactions and a mechanism for RSL's ability to promote receptor cross-linking and cell aggregation.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Molecular and Medical Genetics, University of Toronto, Toronto, Ontario M5S 1A8, Canada.