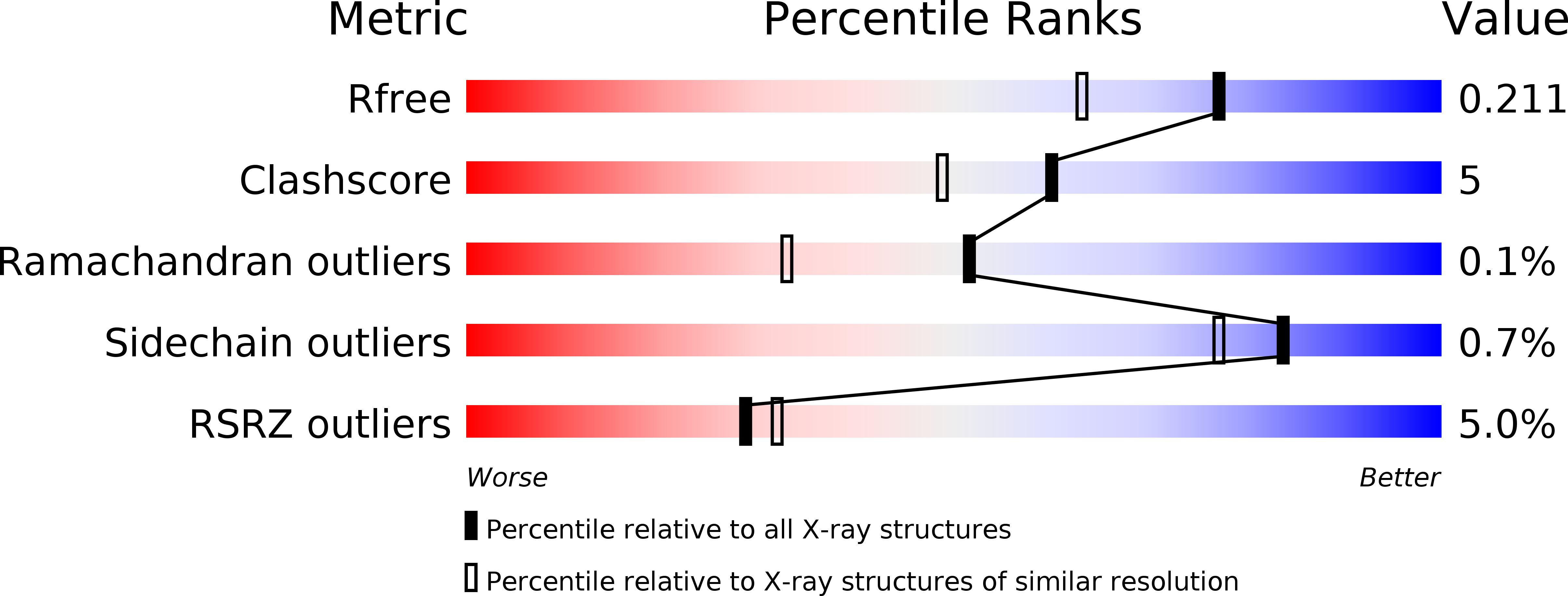
Crystal Structures of the First Condensation Domain of CDA Synthetase Suggest Conformational Changes during the Synthetic Cycle of Nonribosomal Peptide Synthetases.
Bloudoff, K., Rodionov, D., Schmeing, T.M.(2013) J Mol Biol 425: 3137-3150
- PubMed: 23756159
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2013.06.003
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4JN3, 4JN5 - PubMed Abstract:
Nonribosomal peptide synthetases (NRPSs) are large modular macromolecular machines that produce small peptide molecules with wide-ranging biological activities, such as antibiotics and green chemicals. The condensation (C) domain is responsible for amide bond formation, the central chemical step in nonribosomal peptide synthesis. Here we present two crystal structures of the first condensation domain of the calcium-dependent antibiotic (CDA) synthetase (CDA-C1) from Streptomyces coelicolor, determined at resolutions 1.8Å and 2.4Å. The conformations adopted by CDA-C1 are quite similar in these two structures yet distinct from those seen in other NRPS C domain structures. HPLC-based reaction assays show that this CDA-C1 construct is catalytically active, and small-angle X-ray scattering experiments suggest that the conformation observed in these crystal structures could faithfully represent the conformation in solution. We have performed targeted molecular dynamics simulations, normal mode analyses and energy-minimized linear interpolation to investigate the conformational changes required to transition between the observed structures. We discuss the implications of these conformational changes in the synthetic cycle and of the observation that the "latch" that covers the active site is consistently formed in all studied C domains.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biochemistry, McGill University, Montréal, QC, Canada H3G 0B1.