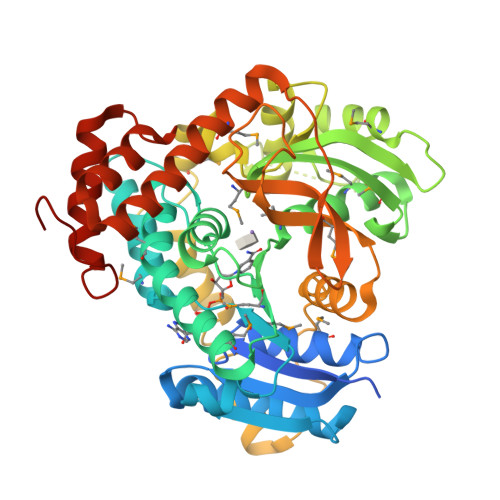
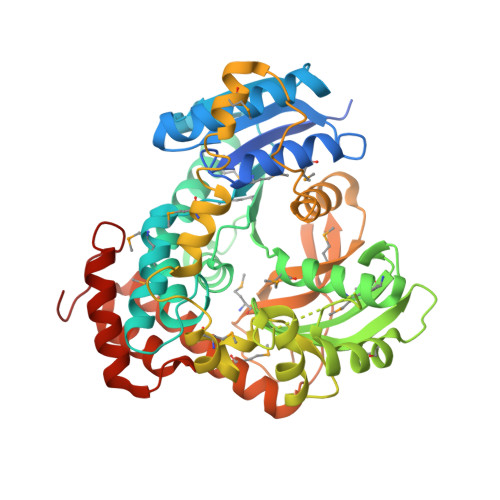
Novel Catalytic Mechanism of Glycoside Hydrolysis Based on the Structure of an NAD(+)/Mn(2+)-Dependent Phospho-alpha-Glucosidase from Bacillus subtilis.
Rajan, S.S., Yang, X., Collart, F., Yip, V.L., Withers, S.G., Varrot, A., Thompson, J., Davies, G.J., Anderson, W.F.(2004) Structure 12: 1619-1629
- PubMed: 15341727
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.str.2004.06.020
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1U8X - PubMed Abstract:
GlvA, a 6-phospho-alpha-glucosidase from Bacillus subtilis, catalyzes the hydrolysis of maltose-6'-phosphate and belongs to glycoside hydrolase family GH4. GH4 enzymes are unique in their requirement for NAD(H) and a divalent metal for activity. We have determined the crystal structure of GlvA in complex with its ligands to 2.05 A resolution. Analyses of the active site architecture, in conjunction with mechanistic studies and precedent from the nucleotide diphosphate hexose dehydratases and other systems, suggest a novel mechanism of glycoside hydrolysis by GlvA that involves both the NAD(H) and the metal.
Organizational Affiliation:
Molecular Pharmacology and Biological Chemistry, Feinberg School of Medicine, Northwestern University, Chicago, IL 60611, USA.