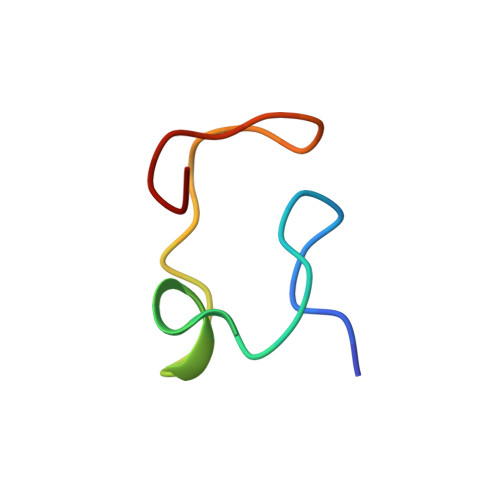
Three-dimensional structure of human [113Cd7]metallothionein-2 in solution determined by nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy.
Messerle, B.A., Schaffer, A., Vasak, M., Kagi, J.H., Wuthrich, K.(1990) J Mol Biology 214: 765-779
- PubMed: 2388267
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-2836(90)90291-S
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1MHU, 2MHU - PubMed Abstract:
The three-dimensional structure of human [113Cd7]metallothionein-2 was determined by nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy in solution. Sequence-specific 1H resonance assignments were obtained using the sequential assignment method. The input for the structure calculations consisted of the metal-cysteine co-ordinative bonds identified with heteronuclear correlation spectroscopy, 1H-1H distance constraints from nuclear Overhauser enhancement spectroscopy, and spin-spin coupling constants 3JHN alpha and 3J alpha beta. The molecule consists of two domains, the beta-domain including amino acid residues 1 to 30 and three metal ions, and the alpha-domain including residues 31 to 61 and four metal ions. The nuclear magnetic resonance data present no evidence for a preferred relative orientation of the two domains. The polypeptide-to-metal co-ordinative bonds in human metallothionein-2 are identical to those in the previously determined solution structures of rat metallothionein-2 and rabbit metallothionein-2a, and the polypeptide conformations in the three proteins are also closely similar.
Organizational Affiliation:
Institut für Molekularbiologie und Biophysik, Hochschule-Hönggerberg, Zürich, Switzerland.