Structural and functional insights into macrophage migration inhibitory factor from Oncomelania hupensis, the intermediate host of Schistosoma japonicum.
Su, Z., Tian, X., Li, H., Wei, Z., Chen, L., Wang, S., Ren, H., Peng, W., Tang, C., Lin, T., Huang, S.(2020) Biochem J 477: 2133-2151
- PubMed: 32484230
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1042/BCJ20200068
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6LKV, 6LKW, 6LR3 - PubMed Abstract:
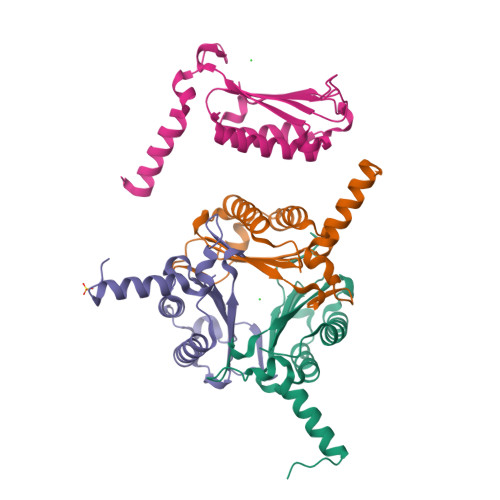
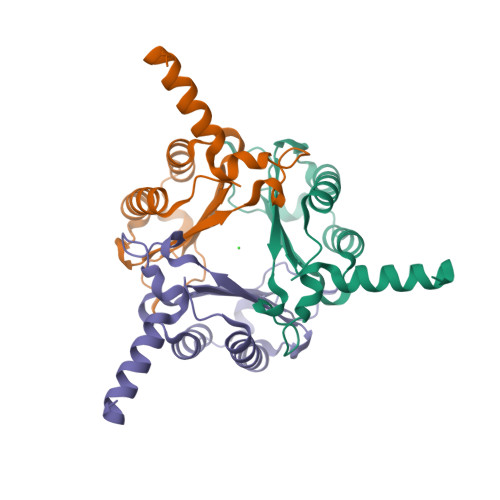
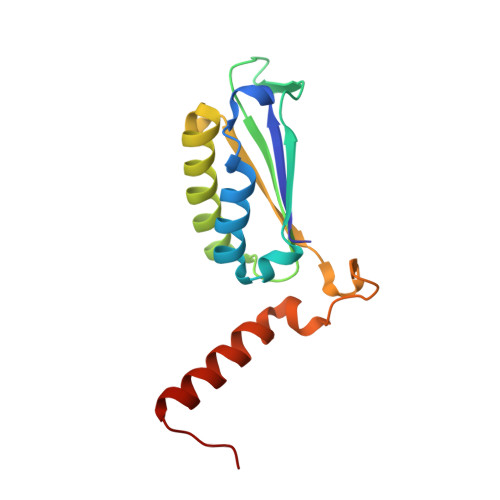
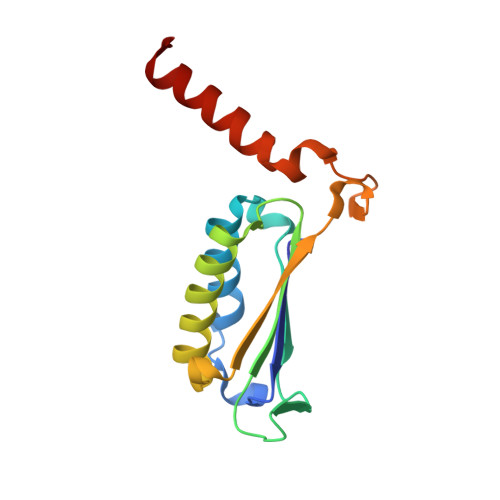
Oncomelania hupensis is the unique intermediate host of Schistosoma japonicum. As an irreplaceable prerequisite in the transmission and prevalence of schistosomiasis japonica, an in-depth study of this obligate host-parasite interaction can provide glimpse into the molecular events in the competition between schistosome infectivity and snail immune resistance. In previous studies, we identified a macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF) from O. hupensis (OhMIF), and showed that it was involved in the snail host immune response to the parasite S. japonicum. Here, we determined the crystal structure of OhMIF and revealed that there were distinct structural differences between the mammalian and O. hupensis MIFs. Noticeably, there was a projecting and structured C-terminus in OhMIF, which not only regulated the MIF's thermostability but was also critical in the activation of its tautomerase activity. Comparative studies between OhMIF and human MIF (hMIF) by analyzing the tautomerase activity, oxidoreductase activity, thermostability, interaction with the receptor CD74 and activation of the ERK signaling pathway demonstrated the functional differences between hMIF and OhMIF. Our data shed a species-specific light on structural, functional, and immunological characteristics of OhMIF and enrich the knowledge on the MIF family.
Organizational Affiliation:
State Key Laboratory of Cellular Stress Biology, Innovation Center for Cell Signaling Network, State-province Joint Engineering Laboratory of Targeted Drugs From Natural Products, School of Life Sciences, Xiamen University, Xiamen, Fujian, China.