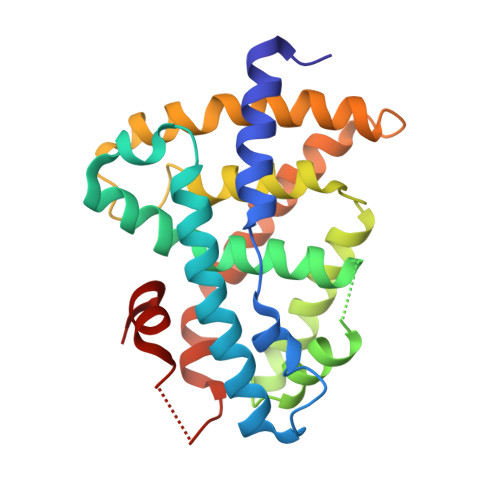
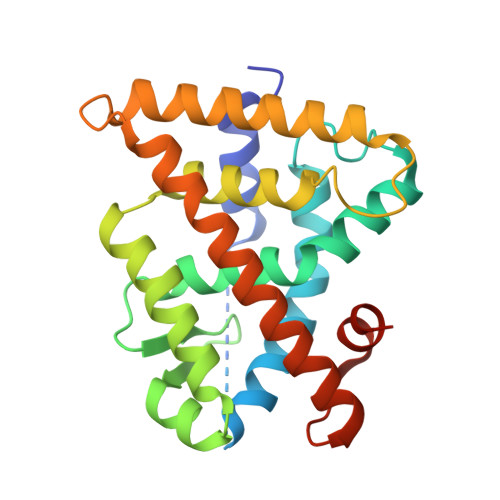
Ligand binding and heterodimerization with retinoid X receptor alpha (RXR alpha ) induce farnesoid X receptor (FXR) conformational changes affecting coactivator binding
Wang, N., Zou, Q., Xu, J., Zhang, J., Liu, J.(2018) J Biol Chem 293: 18180-18191
- PubMed: 30275017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.RA118.004652
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6A5W, 6A5X, 6A5Y, 6A5Z, 6A60 - PubMed Abstract:
Nuclear receptor farnesoid X receptor (FXR) functions as the major bile acid sensor coordinating cholesterol metabolism, lipid homeostasis, and absorption of dietary fats and vitamins. Because of its central role in metabolism, FXR represents an important drug target to manage metabolic and other diseases, such as primary biliary cirrhosis and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. FXR and nuclear receptor retinoid X receptor α (RXRα) form a heterodimer that controls the expression of numerous downstream genes. To date, the structural basis and functional consequences of the FXR/RXR heterodimer interaction have remained unclear. Herein, we present the crystal structures of the heterodimeric complex formed between the ligand-binding domains of human FXR and RXRα. We show that both FXR and RXR bind to the transcriptional coregulator steroid receptor coactivator 1 with higher affinity when they are part of the heterodimer complex than when they are in their respective monomeric states. Furthermore, structural comparisons of the FXR/RXRα heterodimers and the FXR monomers bound with different ligands indicated that both heterodimerization and ligand binding induce conformational changes in the C terminus of helix 11 in FXR that affect the stability of the coactivator binding surface and the coactivator binding in FXR. In summary, our findings shed light on the allosteric signal transduction in the FXR/RXR heterodimer, which may be utilized for future drug development targeting FXR.
Organizational Affiliation:
From the School of Life Sciences, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei 230026, China,; the State Key Laboratory of Respiratory Disease, Guangzhou Institutes of Biomedicine and Health, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Guangzhou 510530, China,; the Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Biocomputing, Guangzhou Institutes of Biomedicine and Health, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Guangzhou 510530, China, and.