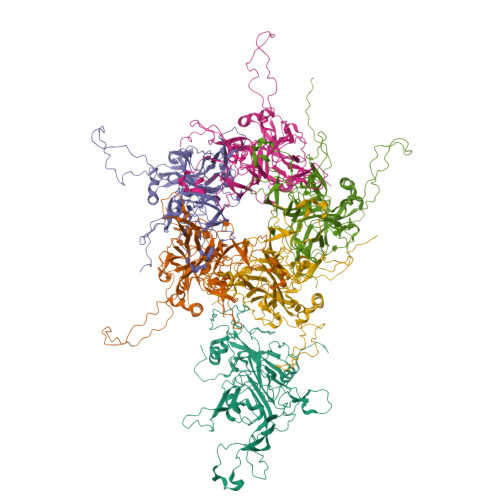
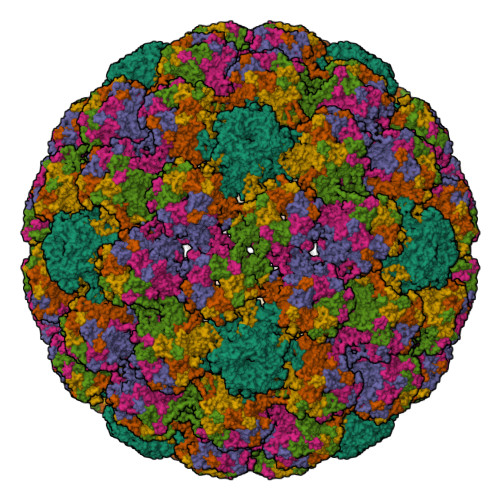
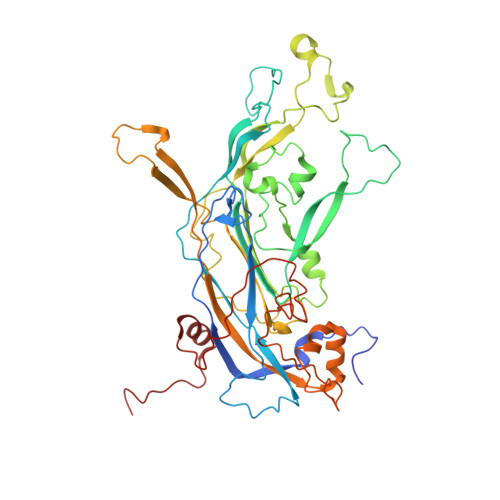
Cryoelectron Microscopy Maps of Human Papillomavirus 16 Reveal L2 Densities and Heparin Binding Site.
Guan, J., Bywaters, S.M., Brendle, S.A., Ashley, R.E., Makhov, A.M., Conway, J.F., Christensen, N.D., Hafenstein, S.(2017) Structure 25: 253-263
- PubMed: 28065506
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.str.2016.12.001
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5KEP, 5KEQ - PubMed Abstract:
Human papillomavirus (HPV) is a significant health burden and leading cause of virus-induced cancers. The current commercial vaccines are genotype specific and provide little therapeutic benefit to patients with existing HPV infections. Host entry mechanisms represent an excellent target for alternative therapeutics, but HPV receptor use, the details of cell attachment, and host entry are inadequately understood. Here we present near-atomic resolution structures of the HPV16 capsid and HPV16 in complex with heparin, both determined from cryoelectron micrographs collected with direct electron detection technology. The structures clarify details of capsid architecture for the first time, including variation in L1 major capsid protein conformation and putative location of L2 minor protein. Heparin binds specifically around the capsid icosahedral vertices and may recapitulate the earliest stage of infection, providing a framework for continuing biochemical, genetic, and biophysical studies.
Organizational Affiliation:
Division of Infectious Diseases, Department of Medicine, Penn State College of Medicine, The Pennsylvania State University College of Medicine, Mail Code H036, 500 University Drive, P.O. Box 850, Hershey, PA 17033-0850, USA.