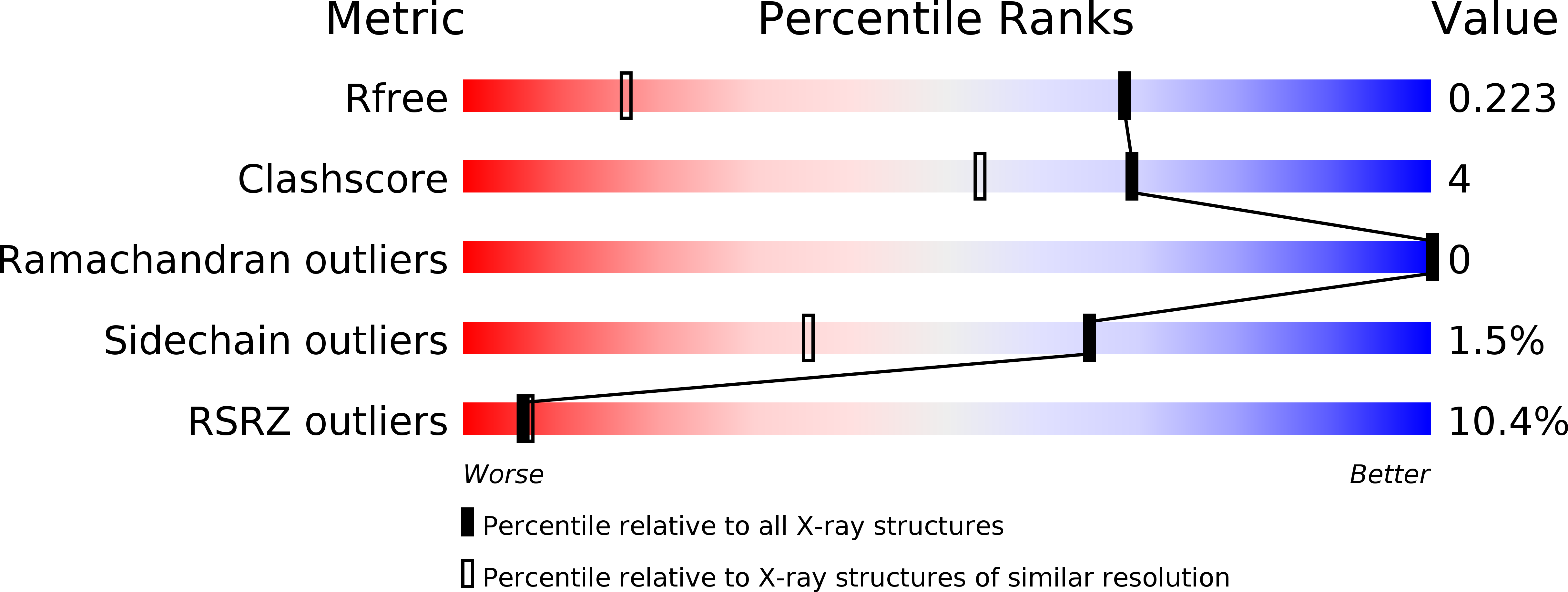
Dissecting Proton Delocalization in an Enzyme's Hydrogen Bond Network with Unnatural Amino Acids.
Wu, Y., Fried, S.D., Boxer, S.G.(2015) Biochemistry 54: 7110-7119
- PubMed: 26571340
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.biochem.5b00958
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5D81, 5D82, 5D83 - PubMed Abstract:
Extended hydrogen bond networks are a common structural motif of enzymes. A recent analysis proposed quantum delocalization of protons as a feature present in the hydrogen bond network spanning a triad of tyrosines (Y(16), Y(32), and Y(57)) in the active site of ketosteroid isomerase (KSI), contributing to its unusual acidity and large isotope shift. In this study, we utilized amber suppression to substitute each tyrosine residue with 3-chlorotyrosine to test the delocalization model and the proton affinity balance in the triad. X-ray crystal structures of each variant demonstrated that the structure, notably the O-O distances within the triad, was unaffected by 3-chlorotyrosine substitutions. The changes in the cluster's acidity and the acidity's isotope dependence in these variants were assessed via UV-vis spectroscopy and the proton sharing pattern among individual residues with (13)C nuclear magnetic resonance. Our data show pKa detuning at each triad residue alters the proton delocalization behavior in the H-bond network. The extra stabilization energy necessary for the unusual acidity mainly comes from the strong interactions between Y(57) and Y(16). This is further enabled by Y(32), which maintains the right geometry and matched proton affinity in the triad. This study provides a rich picture of the energetics of the hydrogen bond network in enzymes for further model refinement.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Chemistry, Stanford University , Stanford, California 94305-5012, United States.