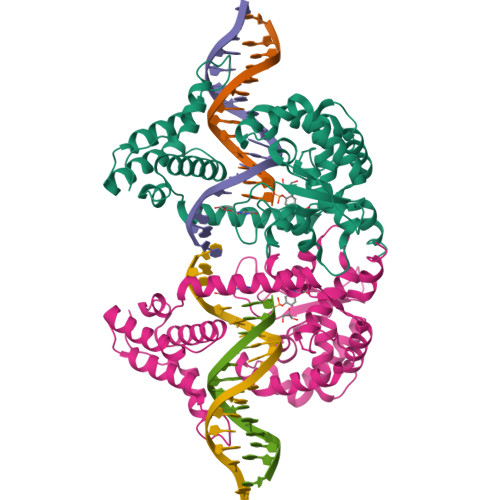
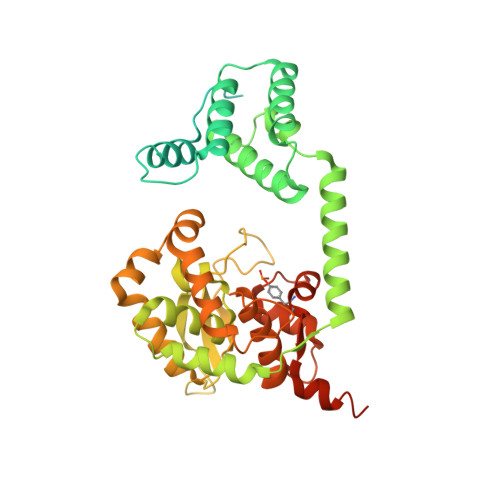
An enzyme-catalyzed multistep DNA refolding mechanism in hairpin telomere formation.
Shi, K., Huang, W.M., Aihara, H.(2013) PLoS Biol 11: e1001472-e1001472
- PubMed: 23382649
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.1001472
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4DWP, 4E0G, 4E0J, 4E0P, 4E0Y, 4E0Z, 4E10 - PubMed Abstract:
Hairpin telomeres of bacterial linear chromosomes are generated by a DNA cutting-rejoining enzyme protelomerase. Protelomerase resolves a concatenated dimer of chromosomes as the last step of chromosome replication, converting a palindromic DNA sequence at the junctions between chromosomes into covalently closed hairpins. The mechanism by which protelomerase transforms a duplex DNA substrate into the hairpin telomeres remains largely unknown. We report here a series of crystal structures of the protelomerase TelA bound to DNA that represent distinct stages along the reaction pathway. The structures suggest that TelA converts a linear duplex substrate into hairpin turns via a transient strand-refolding intermediate that involves DNA-base flipping and wobble base-pairs. The extremely compact di-nucleotide hairpin structure of the product is fully stabilized by TelA prior to strand ligation, which drives the reaction to completion. The enzyme-catalyzed, multistep strand refolding is a novel mechanism in DNA rearrangement reactions.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biochemistry, Molecular Biology and Biophysics, University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, Minnesota, United States of America.