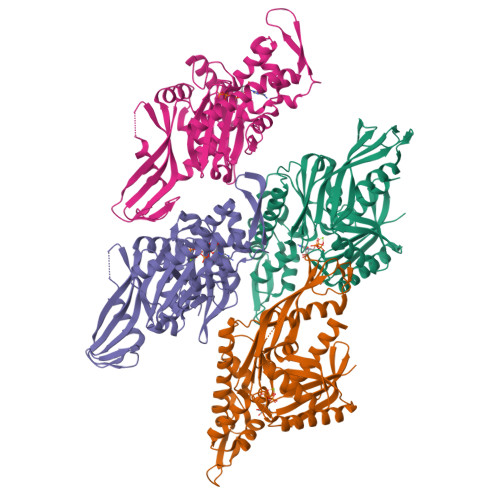
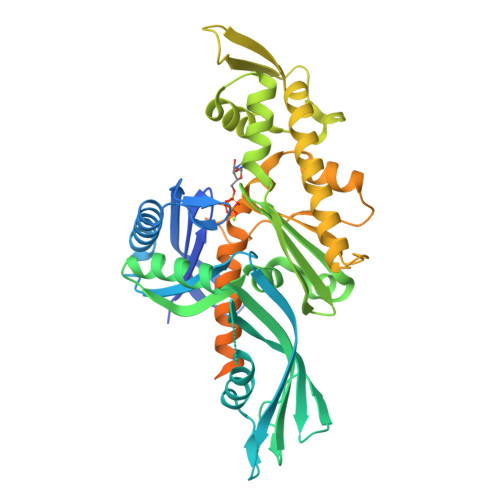
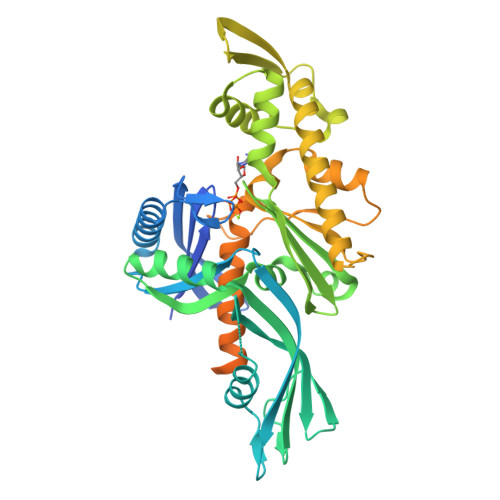
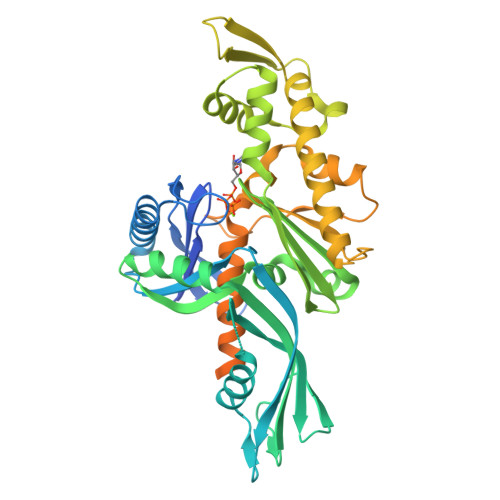
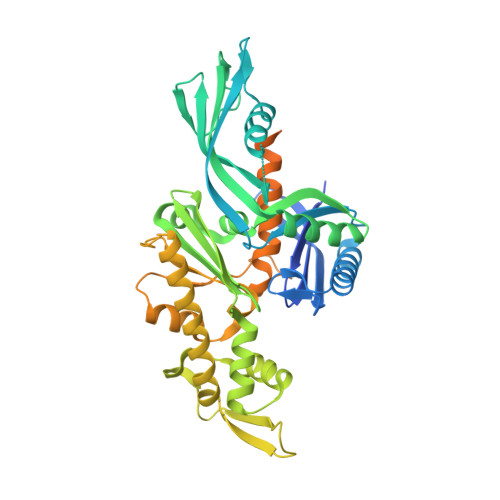
Crystal structure of FtsA from Staphylococcus aureus
Fujita, J., Maeda, Y., Nagao, C., Tsuchiya, Y., Miyazaki, Y., Hirose, M., Mizohata, E., Matsumoto, Y., Inoue, T., Mizuguchi, K., Matsumura, H.(2014) FEBS Lett 588: 1879-1885
- PubMed: 24746687
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.febslet.2014.04.008
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3WQT, 3WQU - PubMed Abstract:
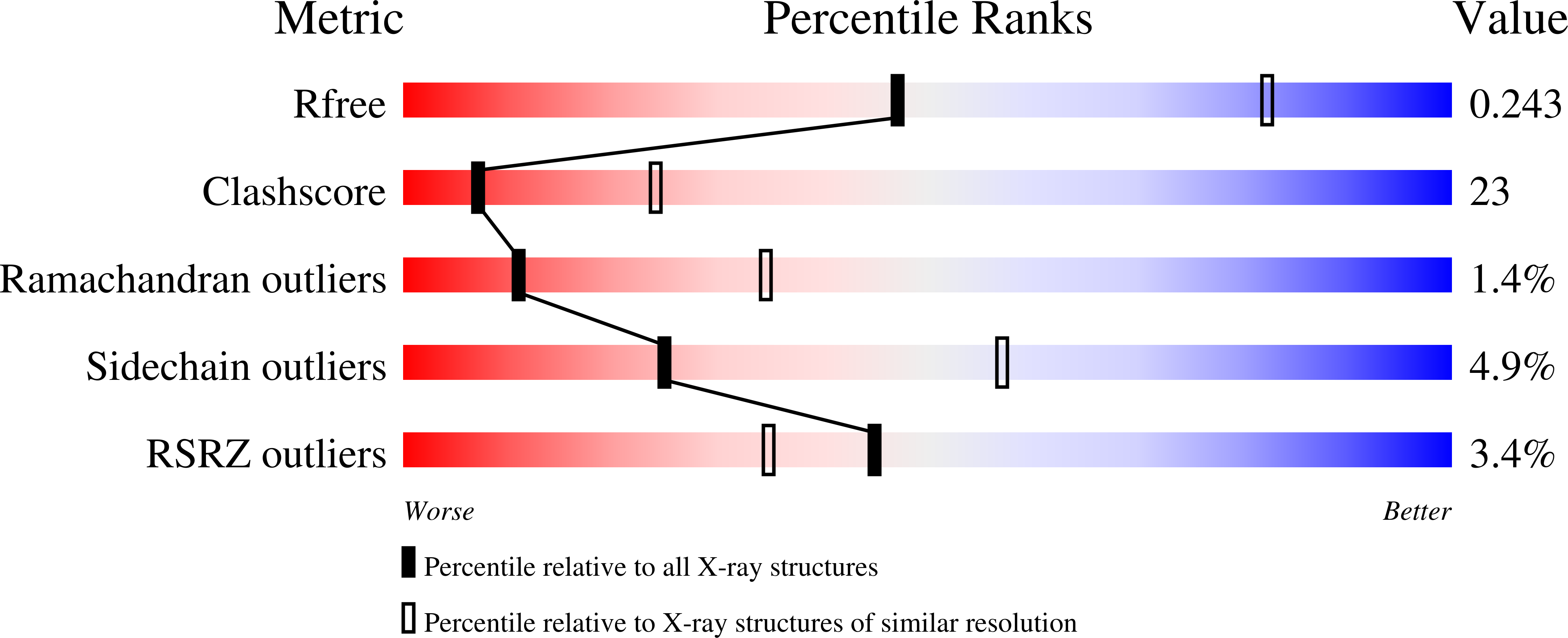
The bacterial cell-division protein FtsA anchors FtsZ to the cytoplasmic membrane. But how FtsA and FtsZ interact during membrane division remains obscure. We have solved 2.2 Å resolution crystal structure for FtsA from Staphylococcus aureus. In the crystals, SaFtsA molecules within the dimer units are twisted, in contrast to the straight filament of FtsA from Thermotoga maritima, and the half of S12-S13 hairpin regions are disordered. We confirmed that SaFtsZ and SaFtsA associate in vitro, and found that SaFtsZ GTPase activity is enhanced by interaction with SaFtsA.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Applied Chemistry, Graduate School of Engineering, Osaka University, 2-1 Yamadaoka, Suita, Osaka 565-0871, Japan.