Domain 4 of the anthrax protective antigen maintains structure and binding to the host receptor CMG2 at low pH
Williams, A.S., Lovell, S., Anbanandam, A., El-Chami, R., Bann, J.G.(2009) Protein Sci 18: 2277-2286
- PubMed: 19722284
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/pro.238
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
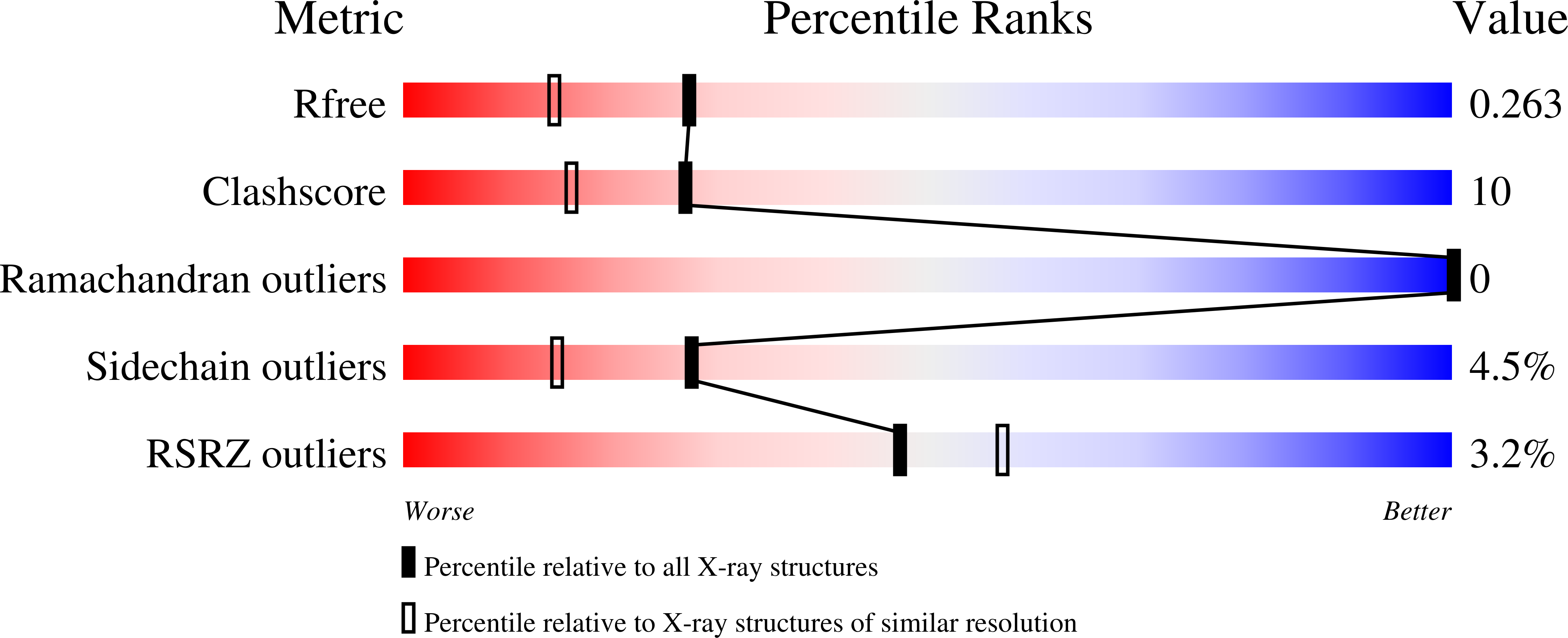
3INO - PubMed Abstract:
Domain 4 of the anthrax protective antigen (PA) plays a key role in cellular receptor recognition as well as in pH-dependent pore formation. We present here the 1.95 A crystal structure of domain 4, which adopts a fold that is identical to that observed in the full-length protein. We have also investigated the structural properties of the isolated domain 4 as a function of pH, as well as the pH-dependence on binding to the von Willebrand factor A domain of capillary morphogenesis protein 2 (CMG2). Our results provide evidence that the isolated domain 4 maintains structure and interactions with CMG2 at pH 5, a pH that is known to cause release of the receptor on conversion of the heptameric prepore (PA(63))(7) to a membrane-spanning pore. Our results suggest that receptor release is not driven solely by a pH-induced unfolding of domain 4.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Chemistry, Wichita State University, Wichita, Kansas 67226, USA.