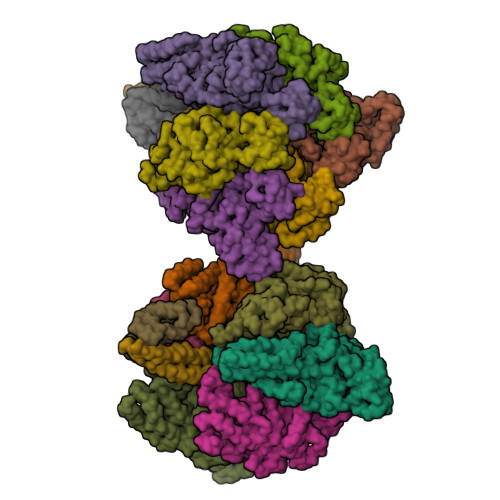
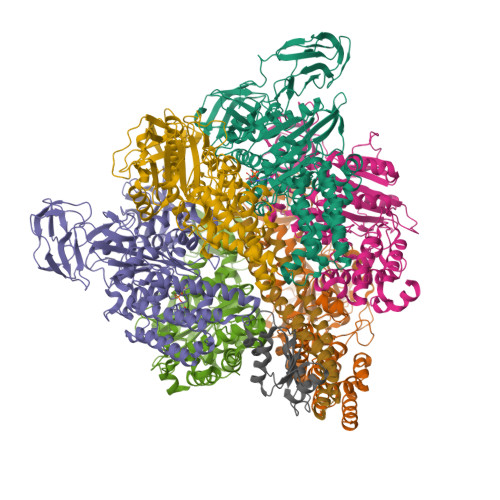
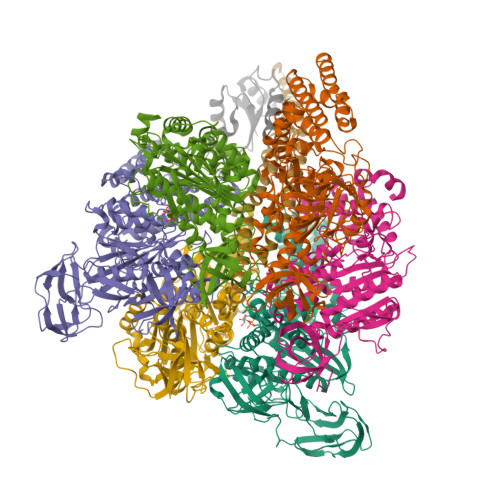
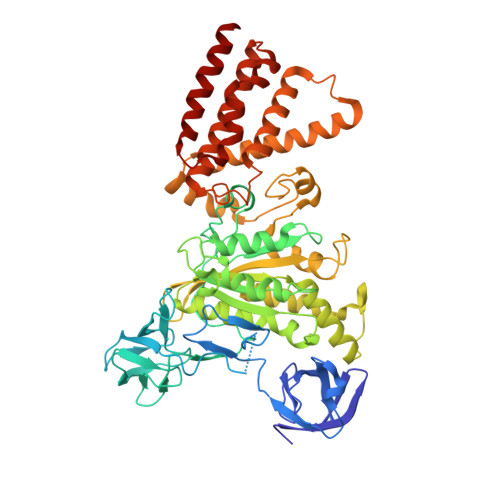
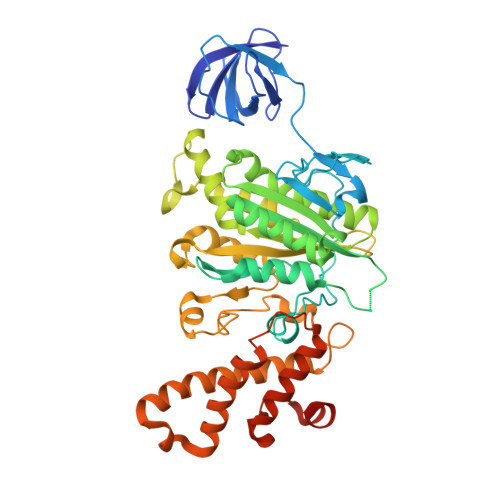
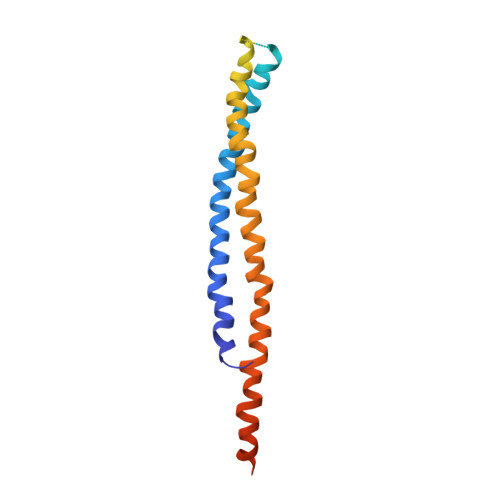
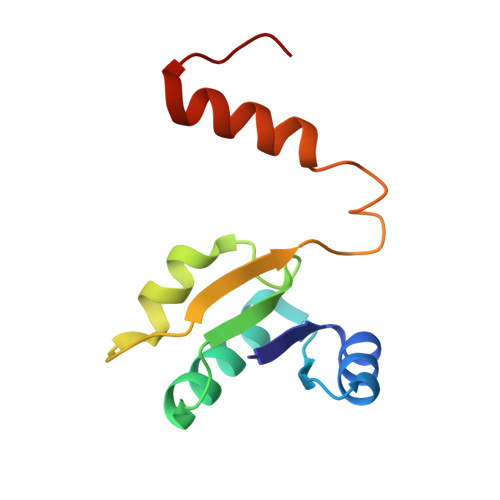
Inter-subunit interaction and quaternary rearrangement defined by the central stalk of prokaryotic V1-ATPase
Numoto, N., Hasegawa, Y., Takeda, K., Miki, K.(2009) EMBO Rep 10: 1228-1234
- PubMed: 19779483
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/embor.2009.202
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3A5C, 3A5D - PubMed Abstract:
V-type ATPases (V-ATPases) are categorized as rotary ATP synthase/ATPase complexes. The V-ATPases are distinct from F-ATPases in terms of their rotation scheme, architecture and subunit composition. However, there is no detailed structural information on V-ATPases despite the abundant biochemical and biophysical research. Here, we report a crystallographic study of V1-ATPase, from Thermus thermophilus, which is a soluble component consisting of A, B, D and F subunits. The structure at 4.5 A resolution reveals inter-subunit interactions and nucleotide binding. In particular, the structure of the central stalk composed of D and F subunits was shown to be characteristic of V1-ATPases. Small conformational changes of respective subunits and significant rearrangement of the quaternary structure observed in the three AB pairs were related to the interaction with the straight central stalk. The rotation mechanism is discussed based on a structural comparison between V1-ATPases and F1-ATPases.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Chemistry, Graduate School of Science, Kyoto University, Sakyo-ku, Kyoto 606-8502, Japan.