Design and characterization of a multimeric DNA binding protein using Sac7d and GCN4 as templates
Wu, S.W., Ko, T.P., Chou, C.C., Wang, A.H.(2005) Proteins 60: 617-628
- PubMed: 16028219
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/prot.20524
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1WVL - PubMed Abstract:
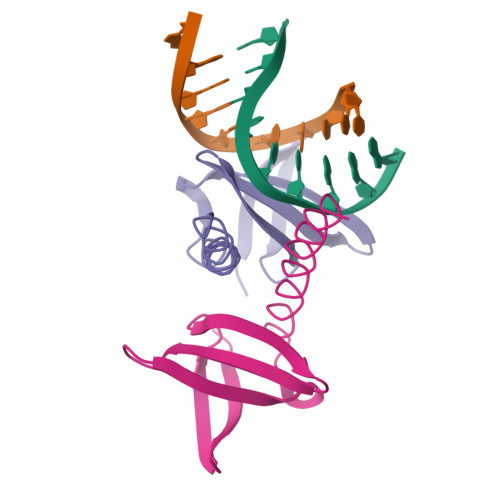
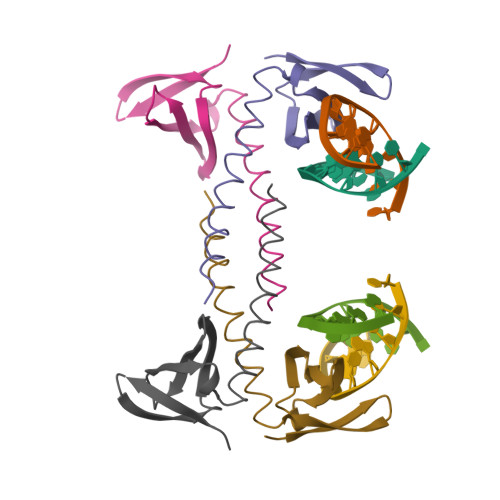
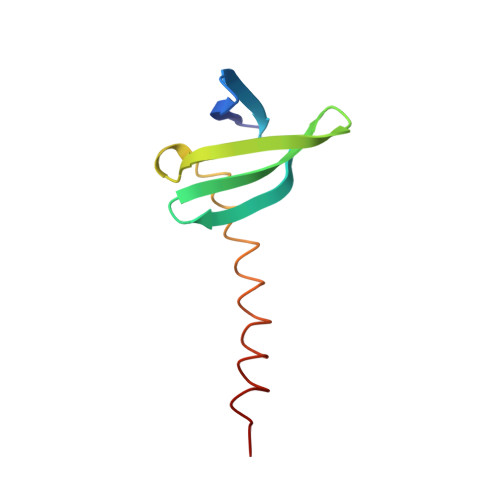
The protein Sac7d belongs to a class of small chromosomal proteins from the hyperthermophilic archaeon Sulfolobus acidocaldarius. Sac7d is extremely stable to heat, acid, and chemical agents. This protein is a monomer and it binds DNA without any particular sequence preference, while inducing a sharp kink in the DNA. By appending a leucine-zipper-like helical peptide derived from the yeast transcriptional activator GCN4 to the C-terminal end of Sac7d, the modified monomers (denoted S7dLZ) are expected to interact with each other via hydrophobic force to form a parallel dimer. The recombinant S7dLZ was expressed in Escherichia coli and purified by heating and ion-exchange chromatography. The formation of dimer was detected by gel-filtration chromatography and chemical cross-link. The results of surface plasmon resonance and circular dichroism experiments showed that the DNA-binding capacity was retained. Furthermore, X-ray diffraction analysis of single crystals of S7dLZ in complex with DNA decamer CCTATATAGG showed that the leucine-zipper segments of S7dLZ were associated into an antiparallel four-helix bundle. There are two DNA fragments bound to each S7dLZ tetramer in the crystal. This model works as a successful template that endows protein a new function without losing original properties.
Organizational Affiliation:
Institute of Biological Chemistry, Academia Sinica, Taipei, Taiwan.