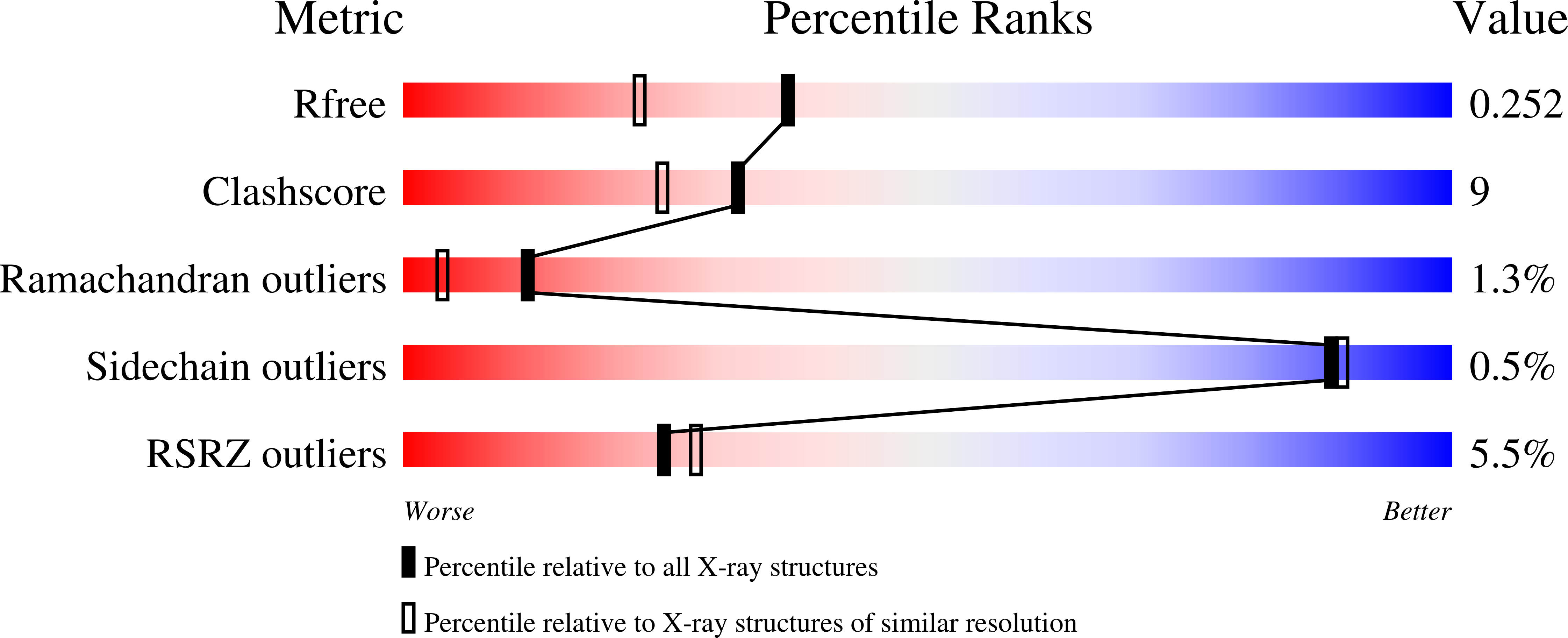
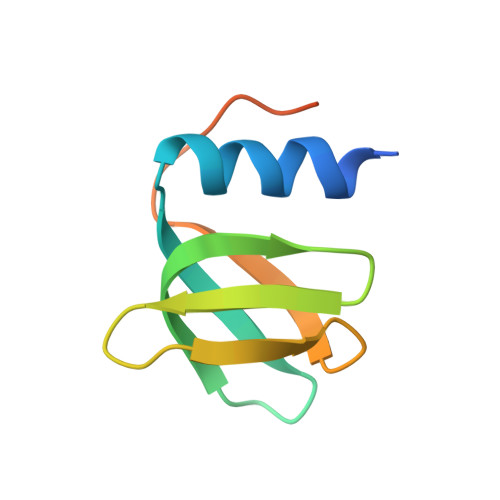
Structure of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Hfq protein.
Nikulin, A., Stolboushkina, E., Perederina, A., Vassilieva, I., Blaesi, U., Moll, I., Kachalova, G., Yokoyama, S., Vassylyev, D., Garber, M., Nikonov, S.(2005) Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr 61: 141-146
- PubMed: 15681864
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1107/S0907444904030008
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1U1S, 1U1T - PubMed Abstract:
The structure of the Hfq protein from Pseudomonas aeruginosa was determined using two different ionic conditions. In both cases the molecules formed identical hexameric rings, but some variations in the crystal packing were revealed. Hfq belongs to the family of Sm/LSm proteins, the members of which can form hexameric as well as heptameric rings. Comparative analysis of known structures of this protein family shows that the fragment of the Sm-fold responsible for oligomerization is strongly structurally conserved. In the heptameric ring, three conserved hydrogen bonds between beta-strands of adjacent molecules hold together the monomers, whereas in the hexameric rings of Hfq an additional conserved inaccessible hydrogen bond between neighbouring monomers is observed.
Organizational Affiliation:
Institute of Protein Research, Russian Academy of Sciences, 142290 Pushchino, Moscow Region, Russia. [email protected]