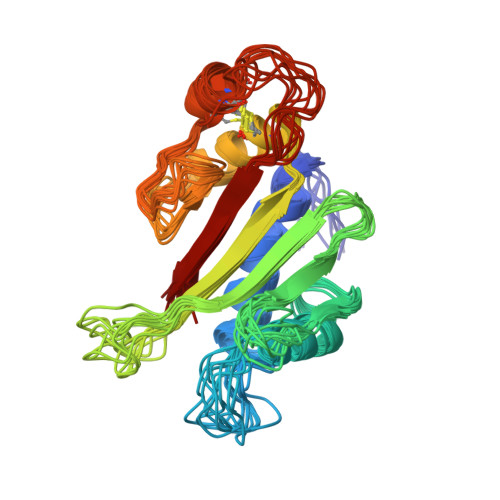
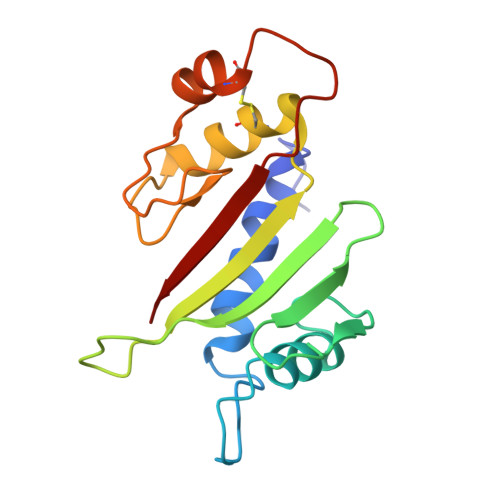
NMR Structure of a Type IVb Pilin from Salmonella typhi and Its Assembly into Pilus
Xu, X.F., Tan, Y.W., Lam, L., Hackett, J., Zhang, M., Mok, Y.K.(2004) J Biological Chem 279: 31599-31605
- PubMed: 15159389
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M404727200
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1Q5F - PubMed Abstract:
The structure of the N-terminal-truncated Type IVb structural pilin (t-PilS) from Salmonella typhi was determined by NMR. Although topologically similar to the recently determined x-ray structure of pilin from Vibrio cholerae toxin-coregulated pilus, the only Type IVb pilin with known structure, t-PilS contains many distinct structural features. The protein contains an extra pair of beta-strands in the N-terminal alphabeta loop that align with the major beta-strands to form a continuous 7-stranded antiparallel beta-sheet. The C-terminal disulfide-bonded region of t-PilS is only half the length of that of toxin-coregulated pilus pilin. A model of S. typhi pilus has been proposed and mutagenesis studies suggested that residues on both the alphabeta loop and the C-terminal disulfide-bonded region of PilS might be involved in binding specificity of the pilus. This model structure reveals an exposed surface between adjacent subunits of PilS that could be a potential binding site for the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biological Sciences, National University of Singapore, Singapore 117543.