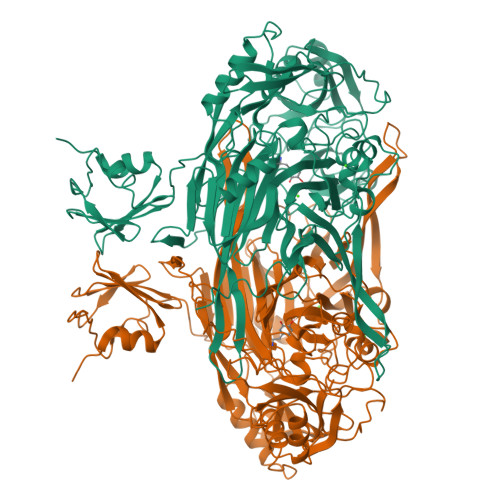
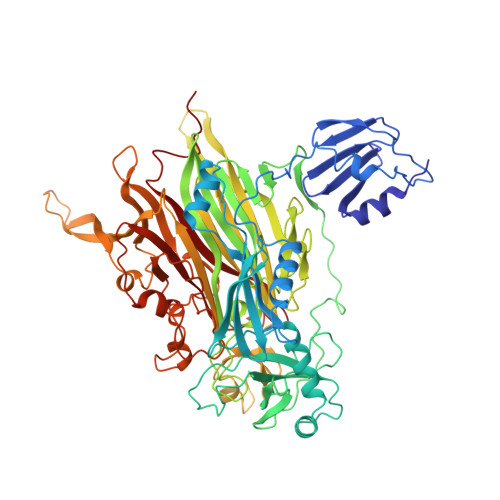
Crystal structure of a quinoenzyme: copper amine oxidase of Escherichia coli at 2 A resolution.
Parsons, M.R., Convery, M.A., Wilmot, C.M., Yadav, K.D., Blakeley, V., Corner, A.S., Phillips, S.E., McPherson, M.J., Knowles, P.F.(1995) Structure 3: 1171-1184
- PubMed: 8591028
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/s0969-2126(01)00253-2
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1OAC - PubMed Abstract:
Copper amine oxidases are a ubiquitous and novel group of quinoenzymes that catalyze the oxidative deamination of primary amines to the corresponding aldehydes, with concomitant reduction of molecular oxygen to hydrogen peroxide. The enzymes are dimers of identical 70-90 kDa subunits, each of which contains a single copper ion and a covalently bound cofactor formed by the post-translational modification of a tyrosine side chain to 2,4,5-trihydroxyphenylalanine quinone (TPQ). The crystal structure of amine oxidase from Escherichia coli has been determined in both an active and an inactive form. The only structural differences are in the active site, where differences in copper coordination geometry and in the position and interactions of the redox cofactor, TPQ, are observed. Each subunit of the mushroom-shaped dimer comprises four domains: a 440 amino acid C-terminal beta sandwich domain, which contains the active site and provides the dimer interface, and three smaller peripheral alpha/beta domains (D1-D3), each of about 100 amino acids. D2 and D3 show remarkable structural and sequence similarity to each other and are conserved throughout the quinoenzyme family. In contrast, D1 is absent from some amine oxidases. The active sites are well buried from solvent and lie some 35 A apart, connected by a pair of beta hairpin arms. The crystal structure of E. coli copper amine oxidase reveals a number of unexpected features and provides a basis for investigating the intriguing similarities and differences in catalytic mechanism of members of this enzyme family. In addition to the three conserved histidines that bind the copper, our studies identify a number of other conserved residues close to the active site, including a candidate for the catalytic base and a fourth conserved histidine which is involved in an interesting intersubunit interaction.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, University of Leeds, UK.