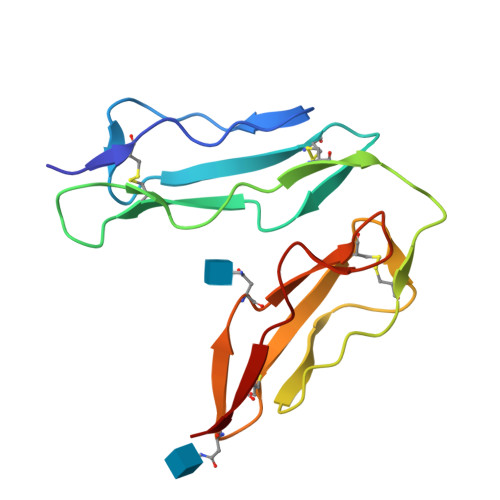
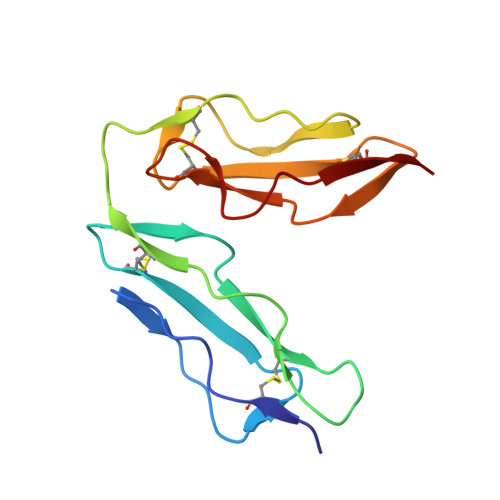
The crystal structure of human CD21: Implications for Epstein-Barr virus and C3d binding.
Prota, A.E., Sage, D.R., Stehle, T., Fingeroth, J.D.(2002) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 99: 10641-10646
- PubMed: 12122212
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.162360499
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1LY2 - PubMed Abstract:
Human complement receptor type 2 (CD21) is the cellular receptor for Epstein-Barr virus (EBV), a human tumor virus. The N-terminal two short consensus repeats (SCR1-SCR2) of the receptor interact with the EBV glycoprotein gp350/220 and also with the natural CD21 ligand C3d. Here we present the crystal structure of the CD21 SCR1-SCR2 fragment in the absence of ligand and demonstrate that it is able to bind EBV. Based on a functional analysis of wild-type and mutant CD21 and molecular modeling, we identify a likely region for EBV attachment and demonstrate that this region is not involved in the interaction with C3d. A comparison with the previously determined structure of CD21 SCR1-SCR2 in complex with C3d shows that, in both cases, CD21 assumes compact V-shaped conformations. However, our analysis reveals a surprising degree of flexibility at the SCR1-SCR2 interface, suggesting interactions between the two domains are not specific. We present evidence that the V-shaped conformation is induced by deglycosylation of the protein, and that physiologic glycosylation of CD21 would result in a more extended conformation, perhaps with additional epitopes for C3d binding.
Organizational Affiliation:
Harvard Medical School, Division of Experimental Medicine and Infectious Diseases, Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Harvard Institutes of Medicine, 4 Blackfan Circle, Boston, MA 02115, USA.