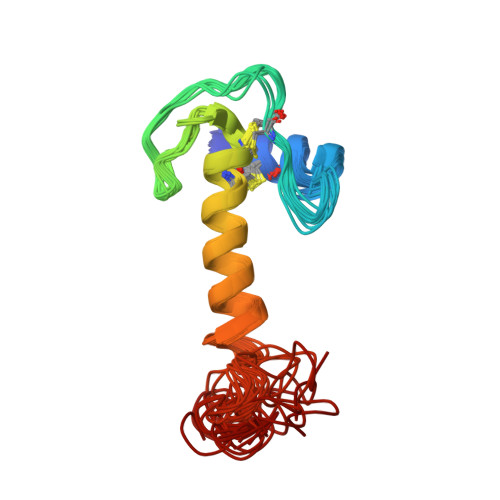
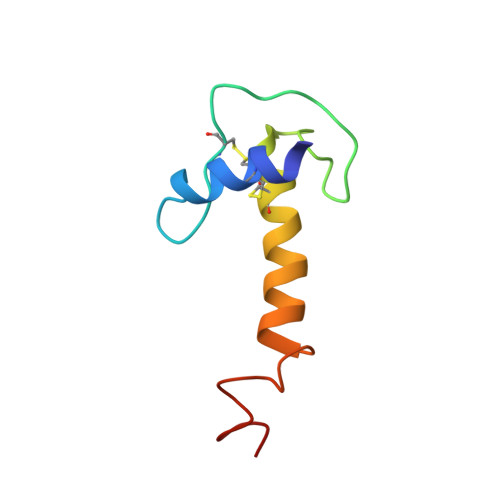
Homologous Lympho-Epithelial Kazal-type Inhibitor Domains Delay Blood Coagulation by Inhibiting Factor X and XI with Differential Specificity.
Ramesh, K., Lama, D., Tan, K.W., Nguyen, V.S., Chew, F.T., Verma, C.S., Mok, Y.K.(2018) Structure 26: 1178-1186.e3
- PubMed: 30017565
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.str.2018.05.018
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5YHN - PubMed Abstract:
Despite being initially identified in the blood filtrate, LEKTI is a 15-domain Kazal-type inhibitor mostly known in the regulation of skin desquamation. In the current study, screening of serine proteases in blood coagulation cascade showed that LEKTI domain 4 has inhibitory activity toward only FXIa, whereas LEKTI domain 6 inhibits both FXIa and FXaB (bovine FXa). Nuclear magnetic resonance structural and dynamic experiments plus molecular dynamics simulation revealed that LEKTI domain 4 has enhanced backbone flexibility at the reactive-site loop. A model of the LEKTI-protease complex revealed that FXaB has a narrower S4 pocket compared with FXIa and hence prefers only small side-chain residues at the P4 position, such as Ala in LEKTI domain 6. Mutational studies combined with a molecular complex model suggest that both a more flexible reactive-site loop and a bulky residue at the P4 position make LEKTI domain 4 a weaker but highly selective inhibitor of FXIa.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biological Sciences, National University of Singapore, 16 Science Drive 4, Singapore 117558, Singapore.