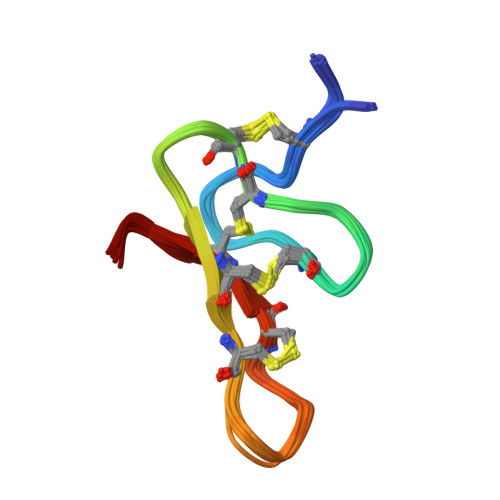
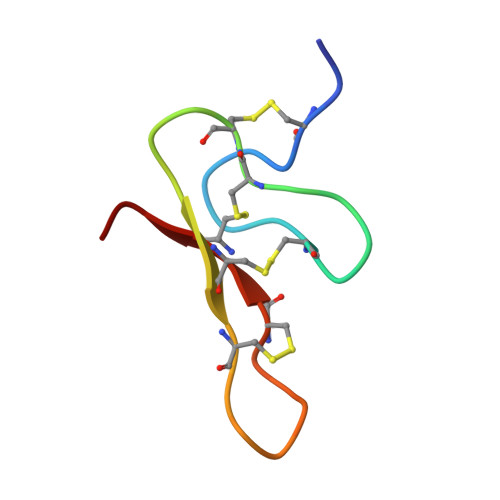
Novel peptide from spider venom inhibits P2X3 receptors and inflammatory pain.
Grishin, E.V., Savchenko, G.A., Vassilevski, A.A., Korolkova, Y.V., Boychuk, Y.A., Viatchenko-Karpinski, V.Y., Nadezhdin, K.D., Arseniev, A.S., Pluzhnikov, K.A., Kulyk, V.B., Voitenko, N.V., Krishtal, O.O.(2010) Ann Neurol 67: 680-683
- PubMed: 20437566
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.21949
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2KGU - PubMed Abstract:
P2X3 purinoreceptors expressed in mammalian sensory neurons play a key role in several processes, including pain perception. From the venom of the Central Asian spider Geolycosa sp., we have isolated a novel peptide, named purotoxin-1 (PT1), which is to our knowledge the first natural molecule exerting powerful and selective inhibitory action on P2X3 receptors. PT1 dramatically slows down the removal of desensitization of these receptors. The peptide demonstrates potent antinociceptive properties in animal models of inflammatory pain.
Organizational Affiliation:
Laboratory of Neuroreceptors and Neuroregulators, Shemyakin-Ovchinnikov Institute of Bioorganic Chemistry, Russian Academy of Sciences, Moscow, Russia.