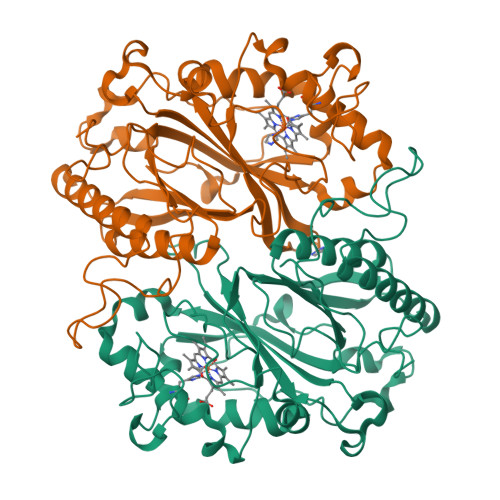
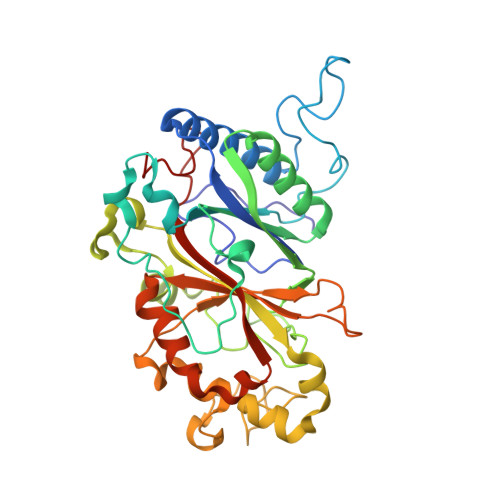
High-throughput structures of protein-ligand complexes at room temperature using serial femtosecond crystallography.
Moreno-Chicano, T., Ebrahim, A., Axford, D., Appleby, M.V., Beale, J.H., Chaplin, A.K., Duyvesteyn, H.M.E., Ghiladi, R.A., Owada, S., Sherrell, D.A., Strange, R.W., Sugimoto, H., Tono, K., Worrall, J.A.R., Owen, R.L., Hough, M.A.(2019) IUCrJ 6: 1074-1085
- PubMed: 31709063
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1107/S2052252519011655
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6I6G, 6I7C, 6I7F, 6QWG - PubMed Abstract:
High-throughput X-ray crystal structures of protein-ligand complexes are critical to pharmaceutical drug development. However, cryocooling of crystals and X-ray radiation damage may distort the observed ligand binding. Serial femtosecond crystallography (SFX) using X-ray free-electron lasers (XFELs) can produce radiation-damage-free room-temperature structures. Ligand-binding studies using SFX have received only modest attention, partly owing to limited beamtime availability and the large quantity of sample that is required per structure determination. Here, a high-throughput approach to determine room-temperature damage-free structures with excellent sample and time efficiency is demonstrated, allowing complexes to be characterized rapidly and without prohibitive sample requirements. This yields high-quality difference density maps allowing unambiguous ligand placement. Crucially, it is demonstrated that ligands similar in size or smaller than those used in fragment-based drug design may be clearly identified in data sets obtained from <1000 diffraction images. This efficiency in both sample and XFEL beamtime opens the door to true high-throughput screening of protein-ligand complexes using SFX.
Organizational Affiliation:
School of Life Sciences, University of Essex, Wivenhoe Park, Colchester CO4 3SQ, England.