Viral infection modulation and neutralization by camelid nanobodies
Desmyter, A., Farenc, C., Mahony, J., Spinelli, S., Bebeacua, C., Blangy, S., Veesler, D., van Sinderen, D., Cambillau, C.(2013) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 110: E1371-E1379
- PubMed: 23530214
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1301336110
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
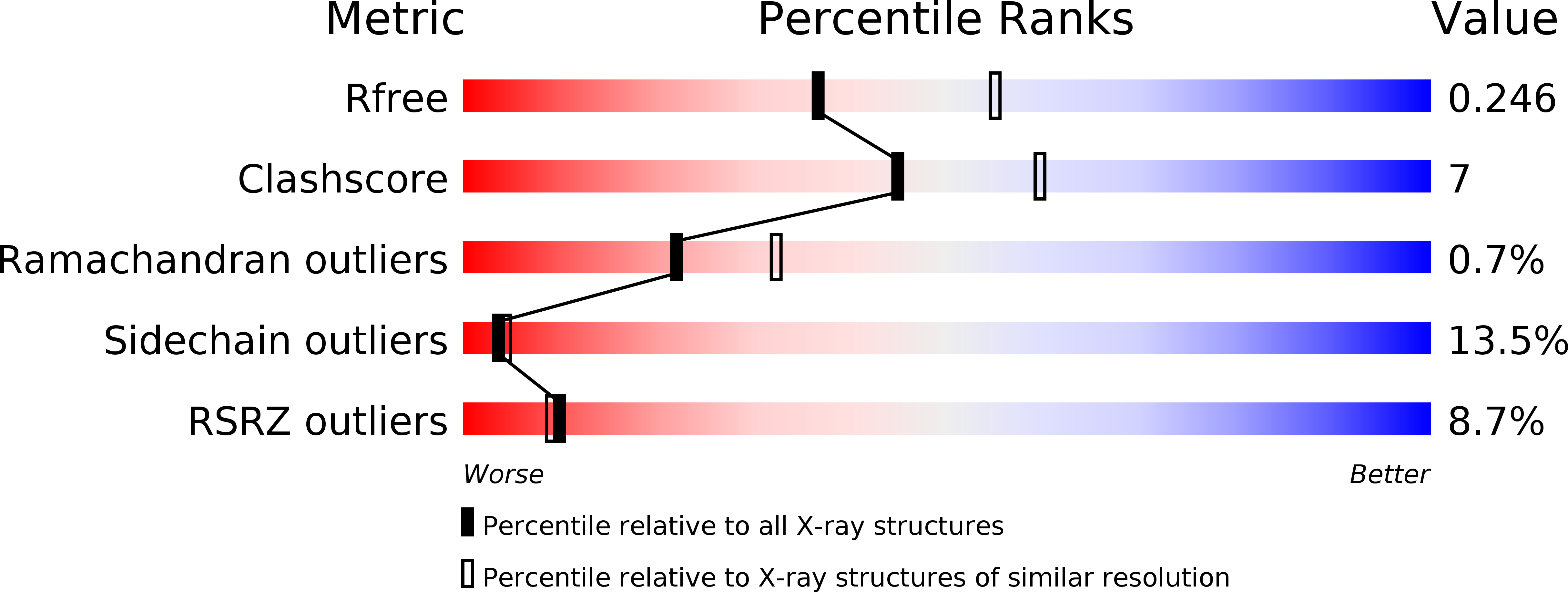
4HEM, 4HEP, 4IOS - PubMed Abstract:
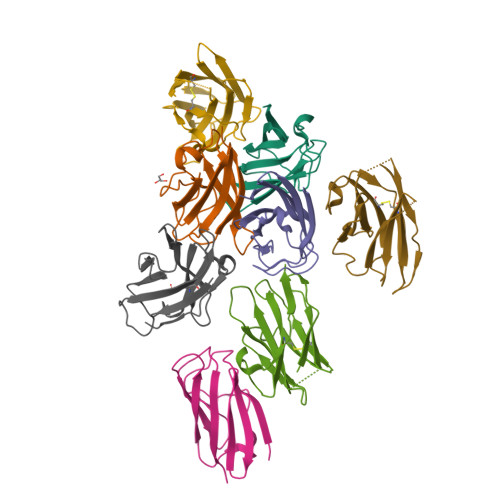
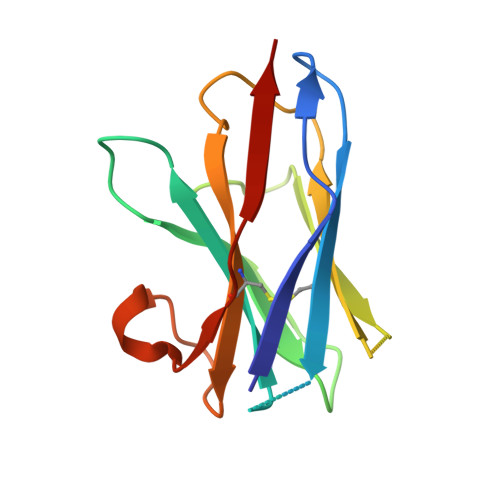
Lactococcal phages belong to a large family of Siphoviridae and infect Lactococcus lactis, a gram-positive bacterium used in commercial dairy fermentations. These phages are believed to recognize and bind specifically to pellicle polysaccharides covering the entire bacterium. The phage TP901-1 baseplate, located at the tip of the tail, harbors 18 trimeric receptor binding proteins (RBPs) promoting adhesion to a specific lactococcal strain. Phage TP901-1 adhesion does not require major conformational changes or Ca(2+), which contrasts other lactococcal phages. Here, we produced and characterized llama nanobodies raised against the purified baseplate and the Tal protein of phage TP901-1 as tools to dissect the molecular determinants of phage TP901-1 infection. Using a set of complementary techniques, surface plasmon resonance, EM, and X-ray crystallography in a hybrid approach, we identified binders to the three components of the baseplate, analyzed their affinity for their targets, and determined their epitopes as well as their functional impact on TP901-1 phage infectivity. We determined the X-ray structures of three nanobodies in complex with the RBP. Two of them bind to the saccharide binding site of the RBP and are able to fully neutralize TP901-1 phage infectivity, even after 15 passages. These results provide clear evidence for a practical use of nanobodies in circumventing lactococcal phages viral infection in dairy fermentation.
Organizational Affiliation:
Architecture et Fonction des Macromolécules Biologiques, Unité Mixte de Recherche 7257 Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique and Aix-Marseille University, 13288 Marseille Cedex 09, France.