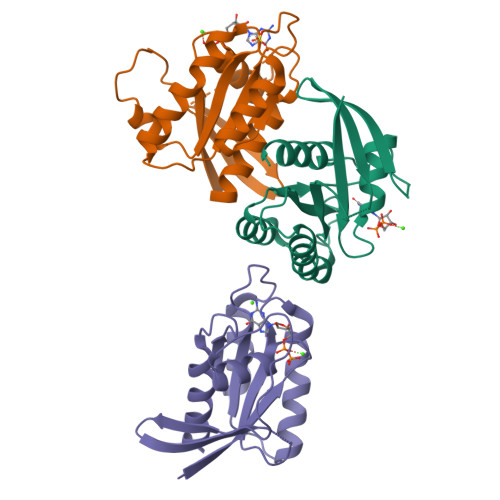
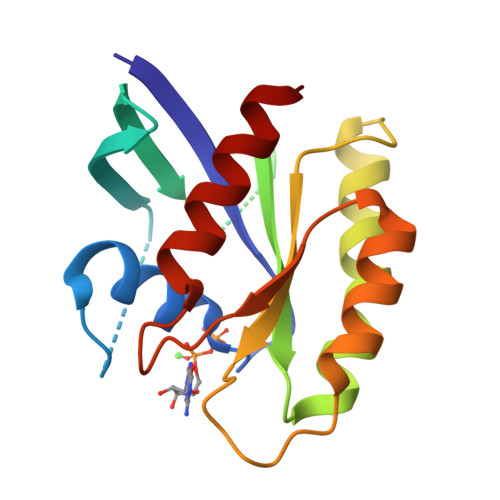
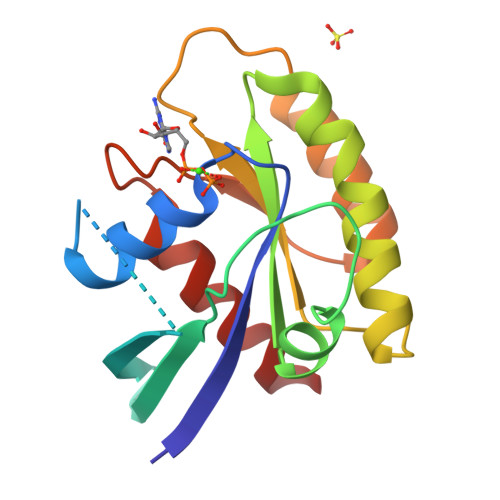
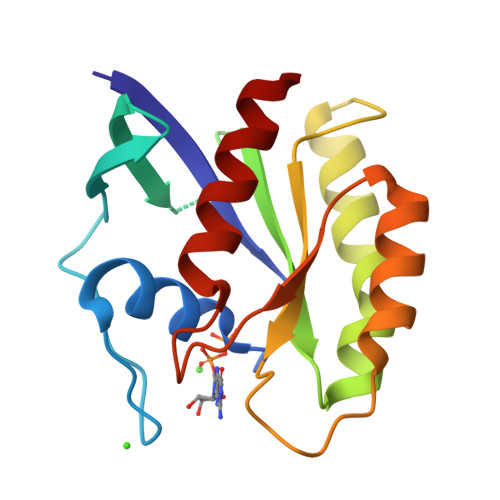
Structure of the Dominant Negative S17N Mutant of Ras
Nassar, N., Singh, K., Garcia-Diaz, M.(2010) Biochemistry 49: 1970-1974
- PubMed: 20131908
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/bi9020742
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3LO5 - PubMed Abstract:
The use of the dominant negative mutant of Ras has been crucial in elucidating the cellular signaling of Ras in response to the activation of various membrane-bound receptors. Although several point mutants of Ras exhibit a dominant negative effect, the asparagine to serine mutation at position 17 (S17N) remains the most popular and the most effective at inhibiting the activation of endogenous Ras. It is now widely accepted that the dominant negative effect is due to the ability of the mutant to sequester upstream activators and its inability to activate downstream effectors. Here, we present the crystal structure of RasS17N in the GDP-bound form. In the three molecules that populate the asymmetric unit, the Mg(2+) ion that normally coordinates the beta-phosphate is absent because of steric hindrance from the Asn17 side chain. Instead, a Ca(2+) ion is coordinating the alpha-phosphate. Also absent from one molecule is electron density for Phe28, a conserved residue that normally stabilizes the nucleotide's guanine base. Except for Phe28, the nucleotide makes conserved interactions with Ras. Combined, the inability of Phe28 to stabilize the guanine base and the absence of a Mg(2+) ion to neutralize the negative charges on the phosphates explain the weaker affinity of GDP for Ras. Our data suggest that the absence of the Mg(2+) should also dramatically affect GTP binding to Ras and the proper positioning of Thr35 necessary for the activation of switch 1 and the binding to downstream effectors, a prerequisite for the triggering of signaling pathways.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Physiology and Biophysics, Stony Brook University, Stony Brook, New York 11794-8661, USA. nicolas.nassar@sunysb.edu