Structural analysis of the complex of Keap1 with a prothymosin alpha peptide
Padmanabhan, B., Nakamura, Y., Yokoyama, S.(2008) Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun 64: 233-238
- PubMed: 18391415
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1107/S1744309108004995
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2Z32 - PubMed Abstract:
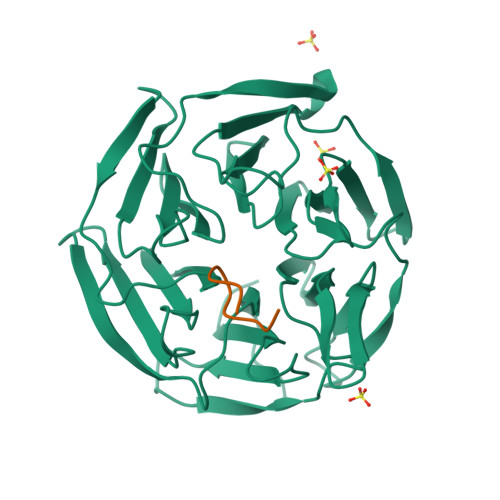
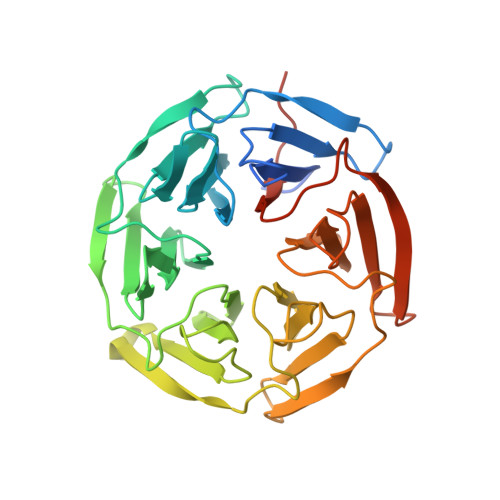
The Nrf2 transcription factor, which plays important roles in oxidative and xenobiotic stress, is negatively regulated by the cytoplasmic repressor Keap1. The beta-propeller/Kelch domain of Keap1, which is formed by the double-glycine repeat and C-terminal region domains (Keap1-DC), interacts directly with the Neh2 domain of Nrf2. The nuclear oncoprotein prothymosin alpha (ProTalpha) also interacts directly with Keap1 and may play a role in the dissociation of the Keap1-Nrf2 complex. The structure of Keap1-DC complexed with a ProTalpha peptide (amino acids 39-54) has been determined at 1.9 A resolution. The Keap1-bound ProTalpha peptide possesses a hairpin conformation and binds to the Keap1 protein at the bottom region of the beta-propeller domain. Complex formation occurs as a consequence of their complementary electrostatic interactions. A comparison of the present structure with recently reported Keap1-DC complex structures revealed that the DLG and ETGE motifs of the Neh2 domain of Nrf2 and the ProTalpha peptide bind to Keap1 in a similar manner but with different binding potencies.
Organizational Affiliation:
Genomic Sciences Center, Yokohama Institute, RIKEN, 1-7-22 Suehiro-cho, Tsurumi, Yokohama 230-0045, Japan. paddy@gsc.riken.jp