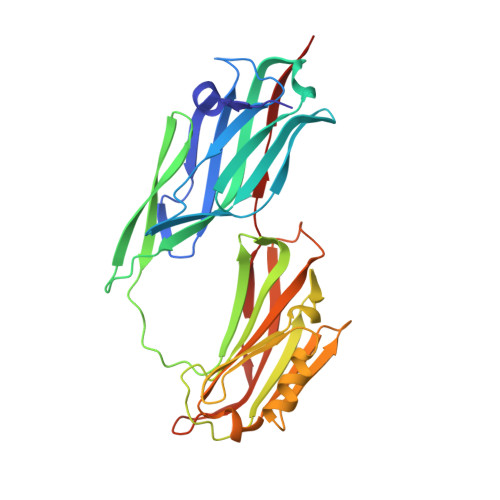
A 'Collagen Hug' model for Staphylococcus aureus CNA binding to collagen.
Zong, Y., Xu, Y., Liang, X., Keene, D.R., Hook, A., Gurusiddappa, S., Hook, M., Narayana, S.V.(2005) EMBO J 24: 4224-4236
- PubMed: 16362049
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.emboj.7600888
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2F68, 2F6A - PubMed Abstract:
The structural basis for the association of eukaryotic and prokaryotic protein receptors and their triple-helical collagen ligand remains poorly understood. Here, we present the crystal structures of a high affinity subsegment of the Staphylococcus aureus collagen-binding CNA as an apo-protein and in complex with a synthetic collagen-like triple helical peptide. The apo-protein structure is composed of two subdomains (N1 and N2), each adopting a variant IgG-fold, and a long linker that connects N1 and N2. The structure is stabilized by hydrophobic inter-domain interactions and by the N2 C-terminal extension that complements a beta-sheet on N1. In the ligand complex, the collagen-like peptide penetrates through a spherical hole formed by the two subdomains and the N1-N2 linker. Based on these two structures we propose a dynamic, multistep binding model, called the 'Collagen Hug' that is uniquely designed to allow multidomain collagen binding proteins to bind their extended rope-like ligand.
Organizational Affiliation:
School of Optometry and Center for Biophysical Sciences and Engineering, University of Alabama at Birmingham, Birmingham, AL 35294, USA.