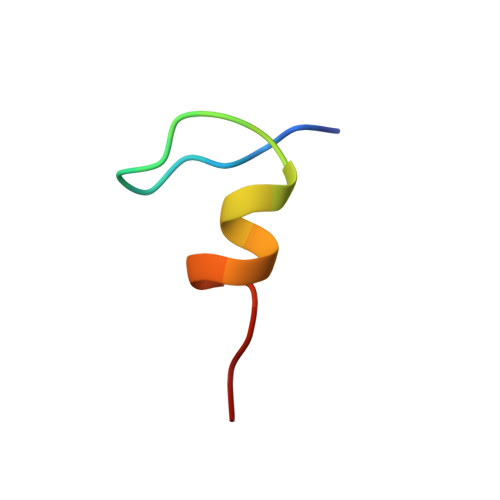
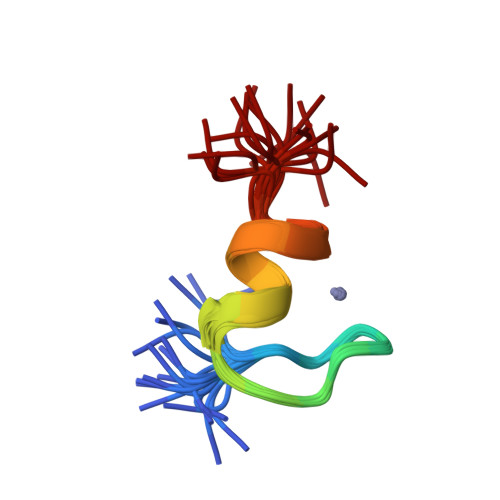
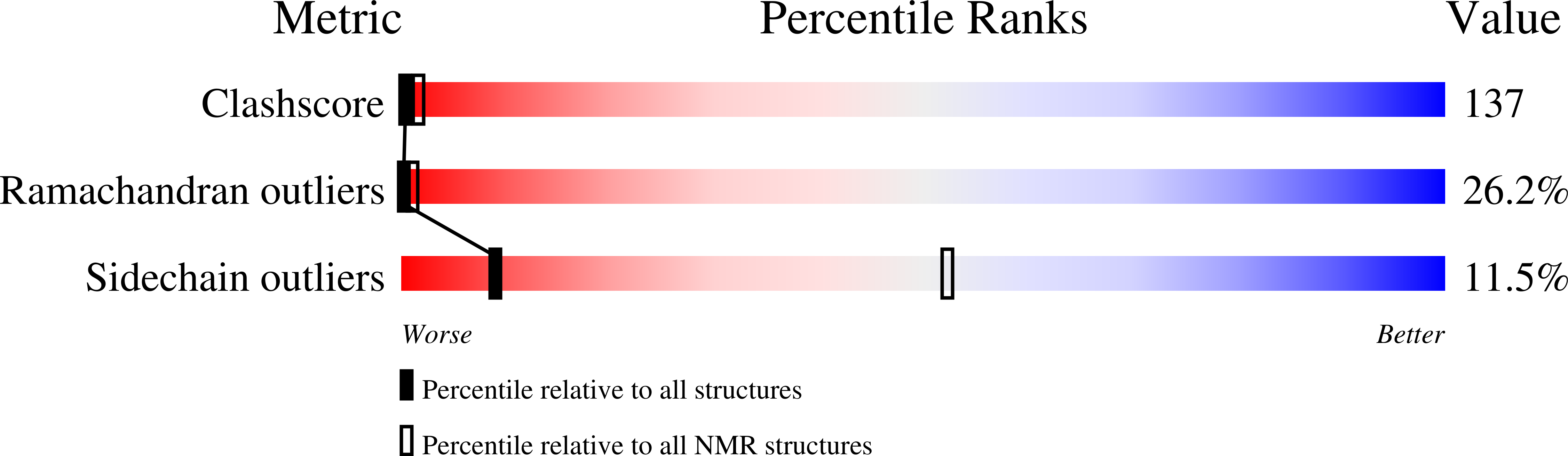NMR structure of the C-terminal domain of SecA in the free state
Matousek, W.M., Alexandrescu, A.T.(2004) Biochim Biophys Acta 1702: 163-171
- PubMed: 15488768
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbapap.2004.08.012
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1TM6 - PubMed Abstract:
SecA is an integral component of the prokaryotic Sec preprotein secretory translocase system. We report here the solution NMR structure of a fragment corresponding to the C-terminal domain of Escherichia coli SecA. In the presence of Zn2+, the fragment adopts a shortened version of the classic betabetaalpha zinc finger fold. The isolated C-terminal domain shows substantial differences from the X-ray structure of a homologous SecA domain bound to the chaperone-like cofactor SecB. The differences between the structures of the free and bound forms suggest that binding to SecB causes a perturbation of the C-terminal domain's intrinsically favored betabetaalpha fold.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Molecular and Cell Biology, University of Connecticut, 91 North Eagleville Road, U-3125, Storrs, CT 06269-3125, USA.